WITH TREX O.E.E. DCAS MEASUREMENTS AND ANALYSIS OF BUSINESS PRODUCTIVITY ANALYSIS:
Üretim proseslerinin ( makinelerin, üretim merkezlerinin, montaj hatlarının vs.) etkinliğini gözlemleyen ve geliştiren en iyi ölçüm metodudur. Endüstride sıkça kullanılan bakım indikatörlerinden ( göstergeler ) birisidir.
Amaç; şirketlerin gereksiz satın alımları yerine mevcut eldeki makine ve ekipmanların performanslarının arttırılmasına odaklanmaktır.
OEE, TPM ( total productive maintenance - toplam verimli bakım ) ve Lean Manufacturing ( yalın üretim) için genelde anahtar veri olarak kullanılır. TPM 'in etkinliğini ölçmede büyük yardımı olur. TPM prosesinin parçası olarak geliştirilmiştir ve birincil performans ölçüm metodudur.
The major maintenance strategies;
TPM ( Total Productive Maintenance )
TQM ( Total Quality Management )
RCM ( Reliability Centred Maintenance )
OEE, combined with the continuous improvement methods (Demming Cycle, DMAIC, FADE, etc.), efficiency of operations, quality and reliability increases in a visible way. Three main components of OEE:
Three main components of OEE:
1. Availability: The rate of machine working time to planned production time. Refers to down time loss. (Reasons: Equipment failures, material shortages, preparation times, change times (such as mold change times).
General objective is to minimize unplanned shutdowns in the production processes. Calculating the downtime costs, provides a better understanding of maintenance issue.
Downtimes can be divided into two complementary parts.
Number of failure measurements, mean time between errors (Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) or Mean Time To Failure (MTTF)) are often widely recommended indicators. These are measure of equipment success and related with functional performance and capacity adequacy. Mean Time to Restore Function (MTRF) of equipment can be divided into pieces.
By analyzing the individual parts of downtime and making small improvements in every step, solution can be find much easier.
2. Performance: The ratio of actual operating speed to the theoretical speed of the machine. Refers to speed loss. (Reasons: The standard use of the material under the wrong feeds, machine corrosion, operator inefficiency, such as short-term downtimes.) And the remaining is net operating time.
3. Quality - The ratio of total solid product to the total production. Refers to quality loss. (Reasons: Initial Wastage, faulty parts, etc.).
In our day, if there is no downtime and wastage, the maximum production rate reach a value of 100% OEE. But this is entirely a theoretical upper limit and the actual value range of factories reach 20% - 65% OEE. Besides so-called "World Class OEE" and accepted as the perfect the values;
Performance
Quality
: %95
: %99.9
OEE : %85,41
In a worldwide research of manufacturing enterprises, OEE value is 60%.
So, wrong assessment of the value of OEE shouldn't be made. The biggest mistake that can be made in interpreting the value of OEE is to ignore the change in the multipliers.
In a business, the values obtained at the first measurements;
Availability = %80, Performance = %99, Quality = %95 >> OEE = %75
The next measurement values;
A = % 95 P = %98 Q =%89 >> OEE = %83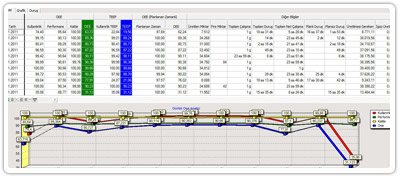 In such a case the interpreter can think the production system is now better than before. But the changes in values must be considered individually. Increase in A corresponding to decrease in P and Q values must be given attention. If the quality (Q) experienced a serious decline, the cost for required quality improvement will increase.
In such a case the interpreter can think the production system is now better than before. But the changes in values must be considered individually. Increase in A corresponding to decrease in P and Q values must be given attention. If the quality (Q) experienced a serious decline, the cost for required quality improvement will increase.
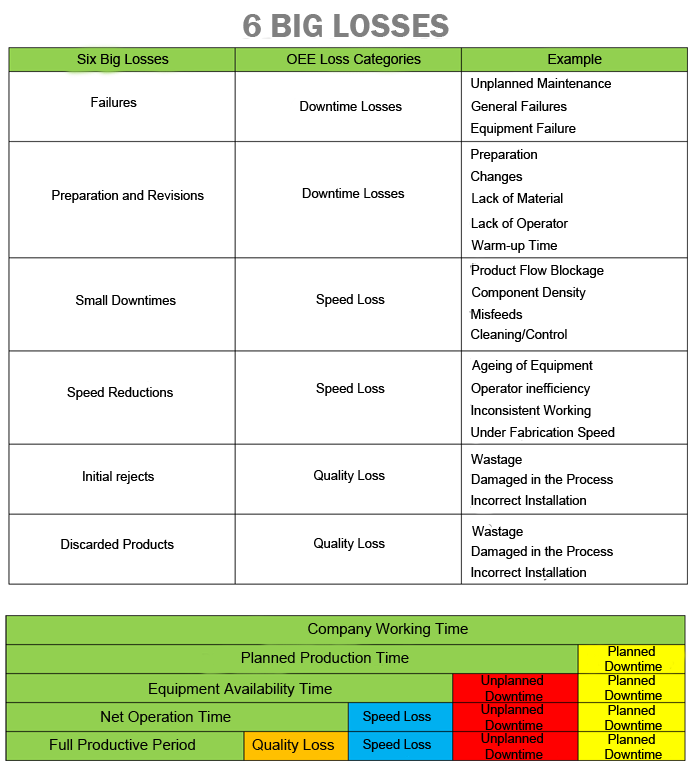
One of the main goals of TPM and OEE programs is to reduce or eliminate efficiency losses in production so-called Six Big Losses. These losses are shown in the table below
TREX DCAS OEE CALCULATION
OEE= Availability x Performance x Quality
Availability = Operation Time / Planned Production Time
Performance = Total Production / Estimated Production
Quality = Number of Solid Parts / Total Number of Parts
Example Application:
Working Time: 8 hours (480 minutes)
Defined breaks: two 15-minute breaks . Total 30 minutes
Lunch Break: 30 minutes
Unplanned downtime: 47 minutes
Theoretical work Rate: 60 parts per minute (per minute should be production quantity.)
Total Produced Parts: 19,271 units
Must be produced (Net Time / Theoretical Operation Time): 373 * 60 = 22 380 units
Number of Rejected parts : 423 units
Planned Production Time = Working Time - Breaks (total) = 480 - (2 * 15 +30) = 420 Minutes
Net Time = Planned production time - Unplanned downtime = 420-47 = 373 Minutes
Total Number of Parts = Total Produced Parts - Number of Rejected parts = 19271-423 = 18 848 units
Availability = Operating time / Planned Production Time = 373/420 = 0.8881 = 88.81%
Performance = Total Produced Parts / Production Required = (19 271 units / 22 380) = 0.8611 = 86.11%
Total Number of Parts Quality = Number of Tracks / Total Produced Parts = 18.848 / 19.271 = 0.9780 = 97.80%
OEE = 0.8881 x 0.8611 x 0.9780 = 74.79% is found.


